What Is Decarbonization? Answering Your Pressing Questions

The goal of zero net carbon emissions has put the spotlight on transitioning to renewable and low carbon energy sources. So what is decarbonization, and how can your business contribute to decreasing the effects of climate change?
What is Decarbonization?

Decarbonization focuses on the reduction of carbon dioxide emissions in the atmosphere, often by switching to renewable energy sources, like solar power and wind power, and increasing energy efficiency.
The ultimate goal of decarbonization is to reach net carbon neutrality: When human efforts balance carbon emissions by removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, typically by stopping emissions from happening at all.
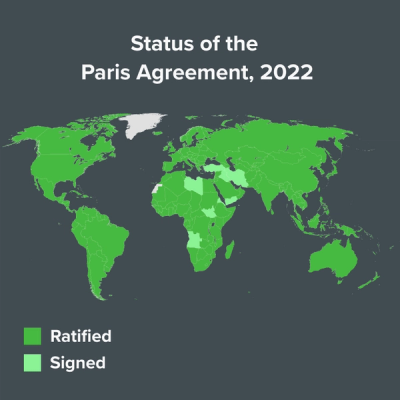
Global efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions include the Paris Agreement, a legally binding international treaty adopted in 2015 to mitigate the effects of climate change. Today, nearly 200 countries have agreed to reduce their usage of fossil fuels to reach net carbon neutrality by 2050, limiting global warming to 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
Why is Decarbonization Important?
Many governments worldwide have declared a climate emergency in response to rising greenhouse gas levels in the atmosphere. According to the World Economic Forum, the complete decarbonization of our global energy systems is the only solution to stabilizing climate change.

To stop the progression of climate change, many governments and companies have made commitments to reduce carbon emissions. For example, one of the top priorities of the Paris Agreement is decarbonization because it plays a critical role in reducing global warming.
For example, Paris has pledged to ban diesel vehicles starting in 2040, while the UK government has committed to achieving net zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050. From energy and transportation to consumer products, businesses across all industries have publicly declared their commitment to net carbon neutrality by 2050.
However, based on current pledges, we are far behind the goals outlined in the Paris Agreement. In the best-case scenario, these efforts will lead to an increase of 2.1 degrees Celsius. But in the worst-case scenario, we can expect a rise in global temperatures of 3.9 degrees Celsius.
How Is Decarbonization Achieved?

Decarbonization involves decreasing the amount of carbon dioxide emitted across industries. Therefore, the path to decarbonization requires a significant overhaul of how industries manufacture and transport goods, including how we produce, store, and distribute energy. The most effective way to reach decarbonization is to use fewer carbon-intense energy sources like fossil fuels. Instead, we must transition to low-carbon emission energy sources and other forms of renewable energy.
For example, many public transportation systems run on carbon-based fuels like diesel and petroleum. However, the growing use of electric vehicles, including commercial vehicles and mass transit buses, offers an opportunity for the transportation sector to reduce carbon emissions significantly.
Some industries are decarbonizing faster than others. Take the power and utilities space, where decarbonization has become a top priority for economic reasons. Many organizations have transitioned from coal to low-cost natural gas, significantly reducing the amount of carbon emissions across the industry. In addition, wind and solar power are some of the cheapest resources available in some areas.
Additionally, social pressure from customers has driven the power sector to offer more eco-friendly products and services, including energy efficiency, net-zero and LEED-certified buildings, smart cities, and much more.
Trends in Decarbonization

The process of decarbonization is rooted in long-term trends, so these efforts are more likely to withstand the effects of an economic downturn or political changes. One of the fastest-growing trends in decarbonization is the emergence of technologies that provide low-carbon-footprint solutions or even suck carbon dioxide right out of the air.
For example, air conditioning releases approximately 117 million metric tons of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere each year. By setting higher efficiency standards for heating and cooling, we can reduce the need for new power plants while cutting emissions and reducing costs.
Scientists have even proposed turning AC units into machines that capture carbon dioxide rather than producing it, transforming it into fuel for vehicles that are difficult to transition to electric power, like cargo ships.
Another emerging trend in decarbonization is self-fertilization. Today, the agriculture industry is heavily dependent on nitrogen-based industrial fertilizers like ammonia, which composes up to 2 percent of global carbon dioxide emissions.
However, the latest in agricultural engineering has made it possible for crops to produce their own fertilizer by mimicking a symbiotic relationship between the plant’s roots and the bacteria that naturally occurs in the soil.
Choose FASTECH for Your Alternative Energy Projects
Decarbonization is a crucial component of a net-zero emissions future. As renewable energy continues to expand, many organizations have become interested in implementing their own alternative energy solutions to reduce their carbon footprint.
At FASTECH, we combine innovative engineering with unparalleled renewable expertise to deliver cutting-edge, sustainable energy sources for municipalities, major oil and gas, industrial energy companies, private organizations, and more.
With over two decades of experience in the energy industry, we develop, construct, and maintain renewable energy sites like hydrogen and CNG fueling stations, industrial infrastructure, and much more.
Contact us today to learn more about how our team of experts can support your renewable energy efforts.